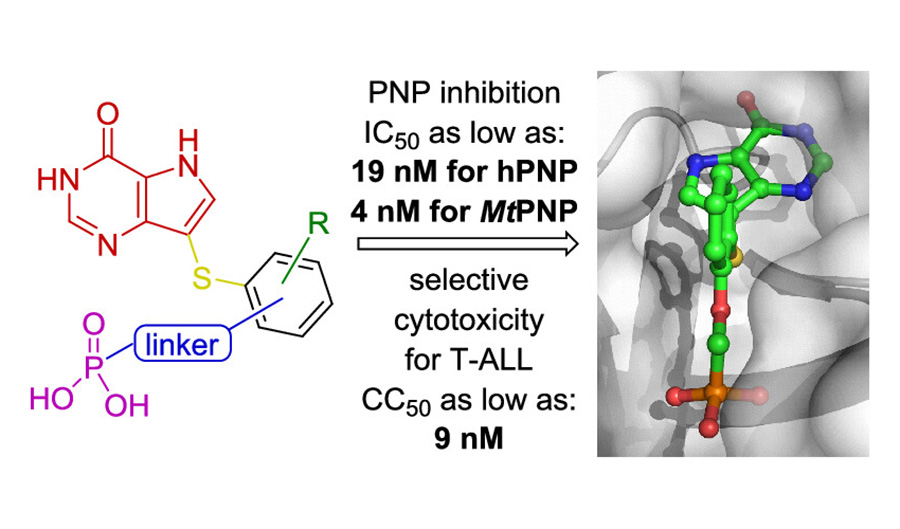
Carbonic anhydrase IX is an enzyme overexpressed in tumors and responsible for the regulation of tumor pH. A multidisciplinary team of scientists from Pavlína Maloy Řezáčová Group at IOCB Prague and other institutes used a structure-assisted design approach to prepare and characterize inhibitors based on carboranes linked to sulfonamides.
The most potent one exhibited strong selectivity to the target cancer-specific carbonic anhydrase isoform with a shrinking effect on the tumor cell cultures and in vivo mice cancer models.
Experimental evidence suggests that this class of inhibitors has a potential for further development of antitumor agents for use in synergistic chemotherapeutical mixtures.
Read the paper:
- Dvořanová, J.; Kugler, M.; Holub, J.; Šícha, V.; Das, V.; Nekvinda, J.; El Anwar, S.; Havránek, M.; Pospíšilová, K.; Fábry, M.; Král, V.; Medvedíková, M.; Matějková, S.; Lišková, B.; Gurská, S.; Džubák, P.; Brynda, J.; Hajdúch, M.; Grüner, B.; Řezáčová, P. Sulfonamido carboranes as highly selective inhibitors of cancer-specific carbonic anhydrase IX. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 200, 112460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112460